The development of cell-initiated degradable hydrogel based on methacrylated alginate applicable to multiple microfabrication technologies†
Abstract
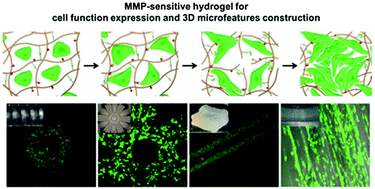
Biomimetic multicellular complex tissues can be obtained via 3D microfabrication approaches, although the lack of active materials that meet the needs of both molding and the maintenance of cell function is the main bottleneck in their application. The development of 3D cell culture platforms, which are suitable for multiple cell types and various microfabrication technologies, would open the way to the biomimetic construction of multicellular complex tissues. In this study, a MMP-sensitive photocrosslinkable hydrogel system based on methacrylated alginate, which is suitable for the survival of multiple cell types and can be employed in a variety of micro-manufacturing technologies, was designed for the construction of 3D microfeatures to meet both the demands of molding and the requirement for biomimetic function. By employing the characteristics of photocrosslinking and ion crosslinking, the gel system was combined with a variety of microfabrication techniques to construct biomimetic microstructures with a spatial distribution of multiple types of cell. The diversity of shapes and cell types in these assemblies, as well as the maintenance of cell activity, collectively show that the functional MMP-sensitive gel system has the potential to be used as a cell culture platform for the construction of tissue microstructures.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 Journal of Materials Chemistry B HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...