The Castanea sativa bur as a new potential ingredient for nutraceutical and cosmetic outcomes: preliminary studies
Abstract
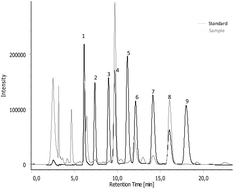
Chestnuts are a common food product in Mediterranean countries, being recognized also for their beneficial effects on human health. Nevertheless, during processing, these fruits generate a large amount of food by-products, such as shells and burs. In the present work, the macronutrient composition, vitamin E profile and amino acid content of the burs were determined in samples from three different Portuguese regions (Minho, Trás-os-Montes and Beira-Alta). The nutritional composition was similar for all samples, being characterised by a high moisture content and low fat amounts. All essential amino acids were present in considerable amounts. Concerning vitamin E, the predominant vitamer was α-tocopherol for the Minho and Beira-Alta samples. The total phenolic compounds were quantified, and the antioxidant activity evaluated in different extracts using two biochemical assays (DPPH˙ and FRAP). All bur extracts showed a high total phenolic content, the highest obtained being that for the Beira-Alta samples. The chestnut bur from Minho showed the highest antioxidant activity in both assays. This study aims to demonstrate the potential of the Castanea sativa bur as a cosmetic and nutraceutical ingredient.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...