Radical cations of phenyl silatrane
Abstract
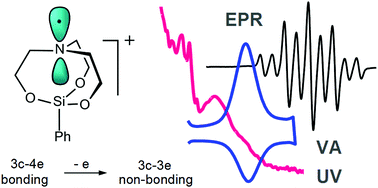
Electrochemical oxidation of phenylsilatrane (1) in CH3CN/0.1 M Bu4NPF6 has been studied by voltammetry, UV-Vis and EPR-coupled spectroelectrochemistry supported by DFT calculations. One-electron withdrawal from the HOMO of 1, formed with a predominant contribution of the atrane N atom to the 3c–4e system, results in a short lived radical cation, in which the atrane nitrogen atom is almost planar and carries most of the spin density showing strong coupling with the protons of the axially directed C–H bonds of the three adjacent α-methylene groups (g = 2.0037, aαHax = 37.93 G, aαHlat = 0.23 G and aβH = 1.8 G). EPR spectroscopy and DFT calculations attest that the unpaired electron in the radical cation does not reside at the Si atom.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Silicon Chemistry: Discoveries and Advances


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...