Photodissociation dynamics of fulvenallene and the fulvenallenyl radical at 248 and 193 nm†
Abstract
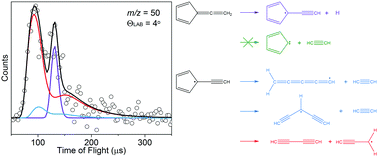
Photofragment translational spectroscopy was used to study the photodissociation of fulvenallene, C7H6, and the fulvenallenyl radical, C7H5, at 248 nm and 193 nm. Starting from fulvenallene, only the H-atom loss channel producing the fulvenallenyl radical, C7H5, was observed. Fulvenallene dissociation occurs on the ground state surface with no exit barrier, and there is good agreement between our experimentally determined photofragment translational energy distribution and a prior distribution for a statistical process. Subsequent absorption at both wavelengths by fulvenallenyl enabled investigation of the photodissociation of this radical. Two channels were observed: C5H3 + C2H2 and C4H2 + C3H3. The photofragment translational energy distributions for these channels are peaked away from 0 kcal mol−1, which is consistent with ground state dissociation over an exit barrier. At 248 nm, the C3H3-loss channel accounted for 85 ± 10% of fulvenallenyl dissociation, while at 193 nm it accounted for 80 ± 15%. The experimental branching between these channels is in reasonable agreement with Rice–Ramsperger–Kassel–Marcus theory calculations, which predict C3H3-loss to account for 70% and 63% of dissociation for 248 nm and 193 nm respectively.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Celebrating our 2018 prize and award winners


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...