A computational study of self-assembled hexapeptide inhibitors against amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregation†
Abstract
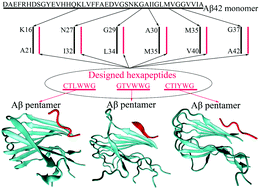
The fibrillation and deposition of amyloid-β (Aβ) peptides in human brains are pathologically linked to Alzheimer's disease (AD). Development of different inhibitors (peptides, organic molecules, and nanoparticles) to prevent Aβ aggregation becomes a promising therapeutic strategy for AD treatment. We recently propose a “like-interacts-like” design principle to computationally design/screen and experimentally validate a new set of hexapeptide inhibitors with completely different sequences from the Aβ sequence. These hexapeptide inhibitors inhibit Aβ aggregation and reduce Aβ-induced cytotoxicity. However, inhibitory mechanisms of these hexapeptides and the underlying interactions between hexapeptides and Aβ remain unclear. Herein we apply multi-scale computational methods (quantum-chemical calculations, molecular docking and explicit-solvent molecular dynamic simulation) to explore the structure, dynamics, and interaction between 3 identified hexapeptides (CTLWWG, GTVWWG, and CTIYWG) and different Aβ-derived fragments and an Aβ17–42 pentamer. When interacting with 6 Aβ-derived fragments, 3 hexapeptide inhibitors show stronger interactions with two lysine-included fragments (16KLVFFA21 and 27NKGAII33) than other fragments, indicating different sequence-specific interactions with Aβ. When interacting with the Aβ17–42 pentamer, the 3 peptides show similar binding modes and interaction mechanisms by preferentially binding to the edge of the Aβ17–42 pentamer to potentially block the Aβ elongation pathway. This work provides structural-based binding information on further modification and optimization of these peptide inhibitors to experimentally enhance their inhibitory abilities against Aβ aggregation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...