Effect of sulfur vacancies on the nitrogen photofixation performance of ternary metal sulfide photocatalysts†
Abstract
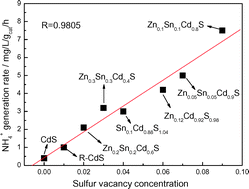
Nitrogen fixation is the second most important chemical process in nature next to photosynthesis. Herein, we report a novel ternary metal sulfide photocatalyst Zn0.1Sn0.1Cd0.8S with outstanding nitrogen photofixation ability under visible light. Characterization results indicate that the actual atomic ratio of the as-prepared ternary metal sulfide is Zn : Sn : Cd : S of 0.11 : 0.12 : 0.88 : 1.12 with many sulfur vacancies, not a mixture of ZnS, SnS2 and CdS. The sulfur vacancies on Zn0.1Sn0.1Cd0.8S not only serve as active sites to adsorb and activate N2 molecules but also promote interfacial charge transfer from Zn0.1Sn0.1Cd0.8S to N2 molecules, thus significantly improving the nitrogen photofixation ability. The other three as-prepared ternary metal sulfides with sulfur vacancies fabricated via the same method exhibit nitrogen photofixation ability, confirming the significantly important role of sulfur vacancies in the nitrogen photofixation process.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...