Robust transparent superamphiphobic coatings on non-fabric flat substrates with inorganic adhesive titania bonded silica†
Abstract
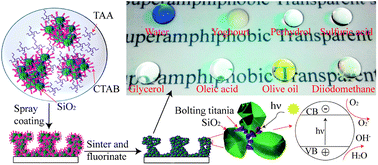
The technological implementation of superamphiphobic surfaces has been largely hindered by the stability issues caused by surface abrasion, corrosion, contamination, etc. Robustness still remains the major challenge for a well-performing superamphiphobic coating. In this study, the simple route of spraying inks containing pre-designed silica, cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) and titanium diisopropoxide bis-2,4-pentanedionate (TAA) is presented to prepare micro–nanostructure films. The mechanical properties of the films are significantly strengthened by titania after the pyrogenic decomposition of TAA, and the films are able to withstand a standard 2H pencil scratching and sand flow impact. The as-made films exhibit excellent super-repellency to various liquids after treatment with 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorodecyltrichlorosilane (PFTS). The static contact angles (SCAs) for water (surface tension 72.1 mN m−1) and dodecane (surface tension 25.3 mN m−1) can reach 166° ± 3° and 153° ± 3°, respectively. On controlling the thickness of the films, the optical transmittance of the films (400 nm thick) can come close to that of glass. Moreover, efficient photocatalytic decomposition of an organic substance attached on the surfaces is demonstrated; this decomposition enables the recovery of the superamphiphobic property of the contaminated films. Thus, the unique properties of robustness, transparency and self-healing, etc., combined with the relatively low cost fabrication, make these superamphiphobic coatings promising in various applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...