Trace Mn decorating nitrogen-doped carbon electrocatalysts for self-powered bio-electro-fenton cells toward simulated wastewater treatment†
Abstract
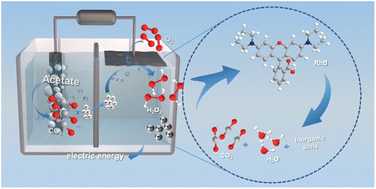
The in situ Fenton reaction utilizing H2O2 has gained significant attention due to its effectiveness in the oxidation of persistent organic pollutants. In this study, we have successfully developed an efficient 2-electron oxygen reduction reaction (2e− ORR) electrocatalyst, Mn-PDA/CNT-2, which exhibits a high H2O2 selectivity of up to 96% within the potential range of 0.65 to 0.85 V vs. RHE in a 0.1 M KOH solution. Moreover, particular emphasis is given to the preparation of an air diffusion floating electrode (ADFE) by incorporating Mn-PDA/CNT-2 onto carbon felt (CF), which enables oxygen in the air to self-drive into the solid state interface of ADFE for the 2e− ORR in bioelectrochemical systems (BESs). Remarkably, the self-aeration ADFE in microbial electrolysis cells (MECs) achieves an impressive maximum current efficiency of 93% for H2O2 production, and the cumulative production of H2O2 reaches a significant amount of 325.18 mg L−1 within a 24 hour period. Additionally, an in situ bio-electro-Fenton system is employed for the degradation of Rhodamine B (RhB). The self-aeration ADFE-MECs system with a Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT) of 6 h demonstrate an effective RhB (6.5 M, pH ≈ 11) degradation rate nearly 90%, accompanied by reduced toxicity in the resulting degradation products.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2023 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...