N-doped carbon xerogels as adsorbents for the removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution†
Abstract
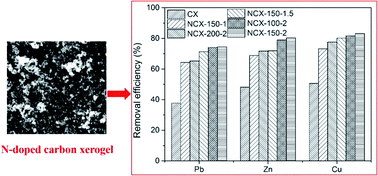
Comparative studies of the textural properties of carbon xerogel (CX) and commercial activated carbon (AC) demonstrated that CX has higher total pore volume and pore diameter, whereas its adsorption capacity for Pb(II) ions in aqueous solution is lower. Herein, the purpose of the present study is to improve the adsorption performance by the introduction of N into the CX matrix on the basis of the extraordinary textural property. Accordingly, the surface chemistry, porous texture, and morphology of the obtained N-doped CX (NCX) were modified. The removal efficiencies of Pb, Zn and Cu by NCX were 1.97, 1.67, and 1.64 times of those by CX, respectively. It was found that the surface density of adsorbed metal ions per unit specific surface area of NCX increased as a linear function with the increase in the N content. The adsorption process of Pb(II) ions followed the pseudo-second-order kinetics and Langmuir model with a maximum adsorption capacity of 83.8 mg g−1, indicating that NCX would be a promising adsorbent for removal of heavy metal ions from water.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...