Photochemically induced radical alkenylation of C(sp3)–H bonds†
Abstract
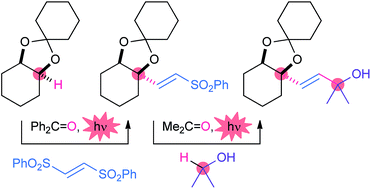
The direct alkenylation of C(sp3)–H bonds was achieved by employing benzophenone and 1,2-bis(phenylsulfonyl)ethylene under photo-irradiation conditions. This simple metal-free reaction enables the substitution of heteroatom-substituted methine, methylene and aliphatic C(sp3)–H bonds by (E)-sulfonylalkene units in a highly chemoselective manner. The derived sulfonylalkenes were further converted in a single step to the prenyl derivatives via a second photo-induced radical substitution and to the pyrrole derivatives via cyclization and aromatization steps. The present protocol thus serves as an efficient method for the direct extension of carbon skeletons for the synthesis of structurally complex natural products and pharmaceuticals.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...