Assembly of alizarin red S/boric acid ultrathin films based on layered double hydroxide for fluorescence turn on detection of tiopronin†
Abstract
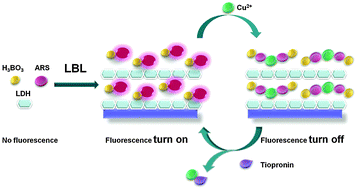
In this study, new facile, economical and fluorescent ultrathin films (UTFs) for detection of tiopronin are developed. The UTFs have been fabricated by combining the alizarin red S–boric acid adduct (ARS–H3BO3) with MgAl layered double hydroxide (LDH) nanoparticles through the layer-by-layer (LBL) assembly technique. UV-vis, fluorescence spectroscopy, XRD, SEM and AFM have been adopted to monitor the assembly process. The UTFs display a uniform morphology and a periodic layered structure. Using ARS as a probe, which does not emit fluorescence by itself but displays fluorescence when complexed with boron, the assembled ARS–H3BO3/LDH UTFs display a high luminescence response to tiopronin. In the presence of Cu2+, the fluorescence of UTFs was quenched, which is attributed to the complexation between Cu2+ and ARS. Upon adding tiopronin to the UTF–Cu system, tiopronin would form a complex with Cu2+ preferentially, leading to the increased fluorescence of UTFs. Based on the above mechanism, a turn-on fluorescent ensemble for tiopronin is developed. A linear response was obtained in the range of 0–80 ng mL−1, with a detection limit of 0.47 ng mL−1. Compared with ARS and other analytes, the tighter binding of tiopronin to Cu2+ led to an assay with high specificity. Therefore, this work provides a facile LBL strategy for the fabrication of a solid state sensor based on ARS dye for detection of tiopronin.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2016 Journal of Materials Chemistry C Hot Papers
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...