Strategies for modulating innate immune activation and protein production of in vitro transcribed mRNAs
Abstract
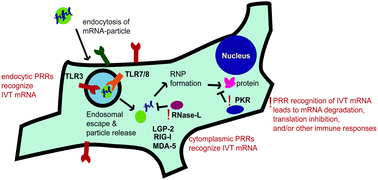
Synthetic mRNA has recently shown great potential as a tool for genetic introduction of proteins. Its utility as a gene carrier has been demonstrated in several studies for both the introduction of therapeutic proteins and subunit vaccines. At one point, synthetic mRNA was believed to be too immunogenic and labile for pharmaceutical purposes. However, the development of several strategies have enabled mRNA technology to overcome these challenges, including incorporation of modified nucleotides, codon optimization of the coding region, incorporation of untranslated regions into the mRNA, and the use of delivery vehicles. While these approaches have been shown to enhance performance of some mRNA constructs, gene-to-gene variation and low efficiency of mRNA protein production are still significant hurdles. Further mechanistic understanding of how these strategies affect protein production and innate immune activation is needed for the widespread adoption for both therapeutic and vaccine applications. This review highlights key studies involved in the development of strategies employed to increase protein expression and control the immunogenicity of synthetic mRNA. Areas in the literature where improved understanding is needed will also be discussed.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Immunological Biomaterials
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...