A systematic study on RNA NMR chemical shift calculation based on the automated fragmentation QM/MM approach
Abstract
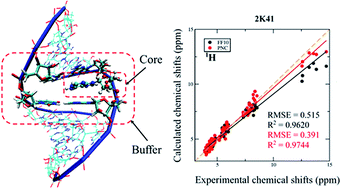
1 H, 13C and 15N NMR chemical shift calculations on RNAs were performed using the automated fragmentation quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (AF-QM/MM) approach. Systematic investigation was carried out to examine the influence of density functionals, force fields, ensemble average and explicit solvent molecules on NMR chemical shift calculations. By comparing the performance of a series of density functionals, the results demonstrate that the mPW1PW91 functional is one of the best functionals for predicting RNA 1H and 13C chemical shifts. This study also shows that the performance of the force fields in describing H-bond strength can be validated by AF-QM/MM calculated imino proton chemical shifts. The polarized nucleic acid-specific charge (PNC) model significantly improves the accuracy of imino hydrogen and nitrogen NMR chemical shift prediction as compared to the FF10 force field, which underscores that the electrostatic polarization effect is critical to stabilizing the hydrogen bonds between base pairs in RNAs. Furthermore, the accuracy of the chemical shift of amino proton can be improved by adding explicit water molecules.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...