Preparation of pH-responsive hollow poly(MAA-co-EGDMA) nanocapsules for drug delivery and ultrasound imaging†
Abstract
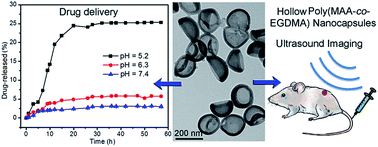
pH-Responsive hollow poly(MAA-co-EGDMA) (abbreviated as HPMAA) copolymer nanocapsules with uniform core size of ∼250 nm and flexible shell thickness of ∼17 nm were synthesized by a hard-template protocol that combined a sol–gel process and surface-initialized polymerization. The silica template was then removed in a 10% HF solution. After further partial surface modification the HPMAA with biocompatible methoxypolyethylene glycol amine (mPEG2000-NH2) and the HPMAA–mPEG nanocapsules displayed negligible hemolytic activity and low cytotoxicity that could be used for pH-responsive delivery of drug (doxorubicin: DOX) and ultrasound imaging. The HPMAA–mPEG nanocapsules have high DOX-loading content (52.4 wt%). The DOX-loaded nanocapsules can be efficiently internalized by cells and controlled release within 20 h under high pH (7.4) condition, resulting substantial inhibition of HeLa cells. Then, the real-time in vivo ultrasound imaging of mice demonstrated that the HPMAA–mPEG nanocapsules can also be used as a novel ultrasound imaging contrast agent.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...