UV-visible and near-infrared active NaGdF4:Yb:Er/Ag/TiO2 nanocomposite for enhanced photocatalytic applications
Abstract
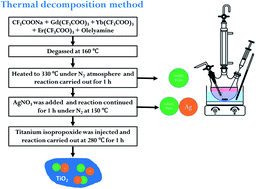
A near infra-red (NIR) active NaGdF4:Yb:Er/Ag/TiO2 nanocomposite photocatalyst was successfully synthesized by a one-pot thermal decomposition method. The composite structure, morphology and elemental mapping of the synthesized NaGdF4:Yb:Er/Ag/TiO2 nanocomposite were characterized by X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy analysis. The energy transfer among NaGdF4:Yb:Er, Ag, and TiO2 was revealed by upconversion photoluminescence measurements at 980 nm. The Ag and NaGdF4 nanoparticles enhanced the visible and NIR light absorption property of the NaGdF4:Yb:Er/Ag/TiO2 nanocomposite. The NIR and UV-visible light induced photocatalytic study of the NaGdF4:Yb:Er/Ag/TiO2 composite was examined by rhodamine B degradation. The energy transfer among NaGdF4:Yb:Er, Ag, and TiO2 significantly influenced the photocatalytic activity under NIR irradiation. The catalysts produced oxidative species during NIR irradiation, which are responsible for the photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B. NaGdF4:Yb:Er/Ag/TiO2 showed photocatalytic activity under NIR and UV-visible radiation (full solar irradiation), which is superior to a UV or visible light active photocatalyst. The study provided a UV-visible and NIR-responsive photocatalyst and its energy transfer mechanism.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...