Reduced graphene oxide/ZnO nanocomposite for application in chemical gas sensors
Abstract
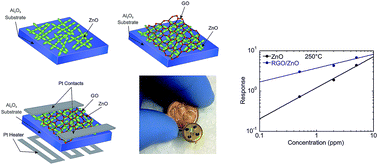
Coupling of graphene-based materials with metal oxide nanostructures is an effective way to obtain composites with improved gas sensing properties. In this work, we prepared a hybrid structure based on graphene oxide (GO) and ZnO nanostructures. The morphological, compositional and structural analyses of the composite material have been investigated using scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction spectroscopy, energy dispersive X-ray analysis and Raman spectroscopy. The gas sensing properties of the obtained structure have been studied towards nitrogen dioxide, hydrogen and methane at relatively low (about 200 °C) operating temperatures. It has been demonstrated that the reduced graphene oxide (RGO)/ZnO composites exhibit 40–50% better response to NO2 and H2 compared to pure ZnO sensors. The obtained results show that the functionalization of the nanostructured ZnO with the RGO sheets is a promising strategy to develop chemical gas sensors with improved gas sensing properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...