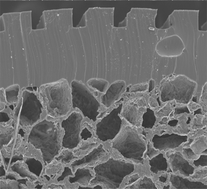
The need for advanced materials in emerging technologies such as tissue engineering has prompted increased research to produce novel biodegradable polymers elastic in nature and mechanically compliant with the host tissue. We have developed a soft biodegradable elastomeric platform biomaterial created from citric acid, maleic anhydride, and 1,8-octanediol, poly(octamethylene maleate (anhydride) citrate) (POMaC), which is able to closely mimic the mechanical properties of a wide range of soft biological tissues. POMaC features a dual crosslinking mechanism, which allows for the option of the crosslinking POMaC using UV irradiation and/or polycondensation to fit the needs of the intended application. The material properties, degradation profiles, and functionalities of POMaC thermoset networks can all be tuned through the monomer ratios and the dual crosslinking mechanism. POMaC polymers displayed an initial modulus between 0.03 and 1.54 MPa, and elongation at break between 48% and 534% strain. In vitro and in vivo evaluation using cell culture and subcutaneous implantation, respectively, confirmed cell and tissue biocompatibility. POMaC biodegradable polymers can also be combined with MEMS technology to fabricate soft and elastic 3D microchanneled scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. The introduction of POMaC will expand the choices of available biodegradable polymeric elastomers. The dual crosslinking mechanism for biodegradable elastomer design should contribute to biomaterials science.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...