Phospholipid–silica mesophases formed in hydroalcoholic solution as precursors of mesoporous silica†
Abstract
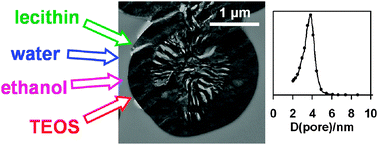
Phosphatidylcholine isotropic mesophases are easily formed by membrane fusion in hydroalcoholic solution in the presence of condensating silica. The transformation of lamellar bilayers into a sponge phase proceeds with the increase of the concentration of ethanol until a monodispersed mesoporous silica with surface area 800 m2 g−1 can be formed by calcination. Natural impurities of lecithin favour the formation of the sponge phase.
- This article is part of the themed collection: The Creative World of Porous Materials

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...