Insights into the molecular interactions of thymoquinone with histone deacetylase: evaluation of the therapeutic intervention potential against breast cancer†
Abstract
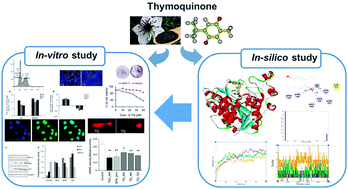
Many HDAC inhibitors have passed through the gateway of clinical trials. However, they have limited therapeutic implications due to their pleiotropic pharmaceutical properties and off-target effects. In view of this, dietary active phytochemicals were evaluated. Based upon the chemical and structural insights of HDAC active pockets, thymoquinone (TQ) was investigated to uncover its active participation in HDAC inhibition. The synergistic analysis of docking and molecular dynamics simulation disclosed the elementary interaction and stability of TQ with human HDACs. The in silico findings were corroborated with an in vitro analysis, demonstrating the efficient role of TQ in the attenuation of global HDAC activity. Furthermore, TQ also elicited downstream effects of HDAC inhibition: reactivation of HDAC target genes (p21 and Maspin), induction of the pro-apoptotic gene Bax, down regulation of the anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-2 and arrest of the cell cycle at the G2/M phase. Finally, the result of a higher cytotoxicity of TQ towards MCF-7 breast cancer cells in comparison to normal cells indicates the potential of TQ to be an anticancer drug.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...