Measurement of the hematocrit using paper-based microfluidic devices†
Abstract
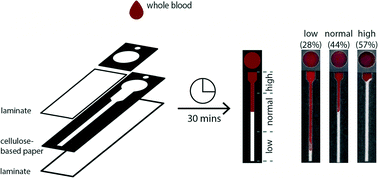
The quantification of blood cells provides critical information about a patient's health status. Sophisticated analytical equipment, such as hematology analyzers, have been developed to perform these measurements, but limited-resource settings often lack the infrastructure required to purchase, operate, and maintain instrumentation. To address these practical challenges, paper-based microfluidic devices have emerged as a platform to develop diagnostic assays specifically for use at the point-of-care. To date, paper-based microfluidic devices have been used broadly in diagnostic assays that apply immunoassay, clinical chemistry, and electrochemistry techniques. The analysis of cells, however, has been largely overlooked. In this communication, we demonstrate a paper-based microfluidic device that enables the controlled transport of red blood cells (RBCs) and the measurement of the hematocrit—the ratio of RBC packed cell volume to total volume of whole blood. The properties of paper, device treatment, and device geometry affect the overall extent and reproducibility of transport of RBCs. Ultimately, we developed an inexpensive (US$0.03 per device) thermometer-styled device where the distance traveled by RBCs is proportional to the hematocrit. These results provide a foundation for the design of paper-based microfluidic devices that enable the separation and detection of cells in limited-resource settings.
- This article is part of the themed collection: RSC papers by GRC Bioanalytical Sensors 2018 Speakers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...