Spectroscopic investigation into the design of solid–acid catalysts for the low temperature dehydration of ethanol†
Abstract
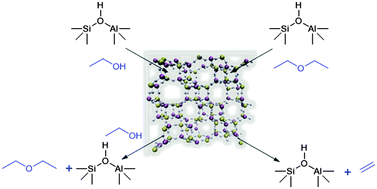
The increased demand for bulk hydrocarbons necessitates research into increasingly sustainable, energy-efficient catalytic processes. Owing to intricately designed structure–property correlations, SAPO-34 has become established as a promising material for the low temperature ethanol dehydration to produce ethylene. However, further optimization of this process requires a precise knowledge of the reaction mechanism at a molecular level. In order to achieve this a range of spectroscopic characterization techniques are required to probe both the interaction with the active site, and also the wider role of the framework. To this end we employ a combination of in situ infra-red and neutron scattering techniques to elucidate the influence of the surface ethoxy species in the activation of both diethyl ether and ethanol, towards the improved formation of ethylene at low temperatures. The combined conclusions of these studies is that the formation of ethylene is the rate determining step, which is of fundamental importance towards the development of this process and the introduction of bio-ethanol as a viable feedstock for ethylene production.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Neutron Scattering in Catalysis and Energy Materials


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...