Electrochemical detection of PCR amplicons of Escherichia coli genome based on DNA nanostructural probes and polyHRP enzyme†
Abstract
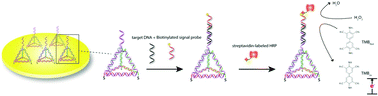
Fast, portable and sensitive analysis of E. coli is becoming an important challenge in many critical fields (e.g., food safety, environmental monitoring and clinical diagnosis). Thus, electrochemical biosensing of PCR amplicons from the bacterial genome has attracted reasonable research attention. In this work, we utilized a 3D DNA tetrahedral probe to establish a “sandwich-type” electrochemical DNA biosensor for sensitive and specific analysis of a 250 bp unpurified PCR amplicon from the uidA gene of the E. coli genome. Asymmetric PCR was used to produce single-stranded PCR products. Streptavidin–polyHRP80 was employed to improve the signal gain during electrochemical detection. We optimized important experimental conditions for DNA sensing, including the streptavidin–polyHRP, the signal probe and the ion strength. Finally, we achieved a remarkable sensitivity of 10 fM synthetic DNA target, and successfully performed the analysis of PCR amplicons from as low as 0.2 pg μL−1 of E. coli genome. Compared with traditional single stranded DNA (ssDNA) probe based detection, our present work demonstrated 3 orders of magnitude improvement in sensitivity. In addition, our electrochemical DNA biosensor was 4 orders of magnitude more sensitive than normal electrophoretic analysis of PCR products. Our work made important progress in DNA nanostructured probe-based biosensors toward application in real applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Emerging Investigators

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...