Optical absorption, charge separation and recombination dynamics in Sn/Pb cocktail perovskite solar cells and their relationships to photovoltaic performances
Abstract
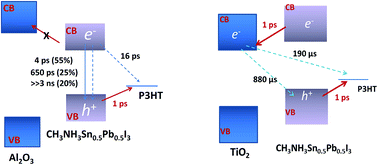
The interest in organometal trihalide perovskite (CH3NH3PbI3)-based solid-state hybrid solar cells has increased in recent years due to the high efficiencies achieved, with a record of over 20%, and the simple low temperature preparation method. Further improvements in the photovoltaic performance can be obtained by increasing the light harvesting in the NIR region up to 1000 nm. Recently, successful energy harvesting up to a wavelength of 1060 nm using Sn/Pb cocktail halide based perovskite materials has been achieved. However, the energy conversion efficiency of such solar cells (less than 10%) is much lower than that of CH3NH3PbI3 based solar cells, which is due to their lower open circuit voltage (Voc) and fill factor (FF). In order to improve this, we need to have a good understanding of the key factors governing the photovoltaic performance of these solar cells, i.e., the optical absorption, the charge separation and the recombination dynamics. Therefore, for this study, we characterized the optical absorption properties, including the bandgap and the Urbach energy, clarified the photoexcited carrier recombination dynamics in Sn/Pb cocktail perovskite (CH3NH3Sn0.5Pb0.5I3) and the charge separation and recombination dynamics at each interface in TiO2/Sn/Pb perovskite/P3HT solar cells, and lastly investigated the relationships between these and the photovoltaic performance.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Perovskite Solar Cells


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...