A novel AgNPs-based colorimetric sensor for rapid detection of Cu2+ or Mn2+via pH control†
Abstract
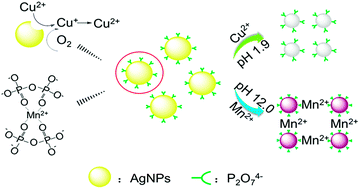
In this study, we propose a new silver nanoparticles (AgNPs)-based colorimetric sensor for rapid detection of Cu2+ or Mn2+ at pH 1.9 or 12.0, respectively. At pH 1.9, the AgNPs stabilized with sodium pyrophosphate (Na4P2O7) and hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC) gradually become smaller in the presence of Cu2+ resulting in a color change of the solution from yellow to colorless. At pH 12.0, however, the AgNPs aggregate immediately in the presence of Mn2+, which induces a color change of the solution from yellow to brown. The incubation time between the detection system and metal ion (Cu2+ or Mn2+) is fixed at 10 min. This mechanism is confirmed using UV-vis spectroscopy, Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Dynamic light scattering (DLS) and Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectrometry (FT-IR). At the optimized experimental conditions, the selectivity of our AgNPs-based detection system is excellent for Cu2+ or Mn2+ compared with other metal ions. The limit of detections (LODs) of Cu2+ and Mn2+ by the naked eye are respectively 0.05 and 0.5 μM, and those by UV-vis spectroscopy are respectively 2.0 and 20 nM. The above LODs are all lower than the corresponding national drinking water standards (16 μM of Cu2+ and 1.8 μM of Mn2+). The applicability of our AgNPs-based colorimetric sensor is also validated by detection of Cu2+ and Mn2+ in tap water and lake water. Therefore, these results reinforce that our AgNPs-based colorimetric sensor is applicable to rapid colorimetric detection of Cu2+ and Mn2+ in complicated real water samples with excellent selectivity and high sensitivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...