A new method for the synthesis of LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 from waste lithium ion batteries
Abstract
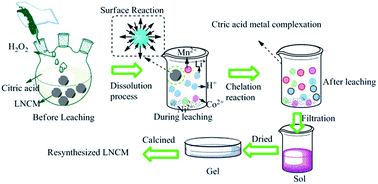
A new process for the synthesis of LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 from recycled valuable metals of waste lithium ion batteries (LIBs) is introduced herein. Citric acid was used as both a leaching and chelating agent. The overall process involves three steps: dissolution of spent lithium ion batteries, sol–gel formation and LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 powder formation. The concentrations of the metal ions, specifically lithium, nickel, manganese, and cobalt in the leachate were determined by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES). The morphologies of the cathode material from waste LIBs before and after leaching, as well as those of the leaching residue and the final products, were observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The structure of the final product was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis. With regards to electrochemical properties, the re-synthesized and fresh-synthesized samples delivered capacities of 147 and 150 mA h g−1, respectively, in the first cycle. The rate performances, high and low temperature discharge performances, and the electrochemical impedance spectra (EIS) are also discussed. This study suggests that the waste lithium ion batteries can be recycled to re-synthesize new cathode materials with good electrochemical performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...