Asymmetric supercapacitors based on carbon nanofibre and polypyrrole/nanocellulose composite electrodes†
Abstract
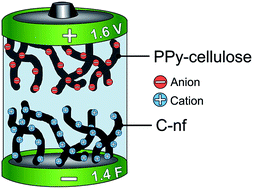
Asymmetric, all-organic supercapacitors (containing an aqueous electrolyte), exhibiting a capacitance of 25 F g−1 (or 2.3 F cm−2) at a current density of 20 mA cm−2 and a maximum cell voltage of 1.6 V, are presented. The devices contain a composite consisting of polypyrrole covered Cladophora cellulose fibres (PPy–cellulose) as the positive electrode while a carbon nanofibre material, obtained by heat treatment of the same PPy–cellulose composite under nitrogen gas flow, serves as the negative electrode. Scanning and transmission electron microscopy combined with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy data show that the heat treatment gives rise to a porous carbon nanofibre material, topologically almost identical to the original PPy–cellulose composite. The specific gravimetric capacitances of the carbon and the PPy–cellulose electrodes were found to be 59 and 146 F g−1, respectively, while the asymmetric supercapacitors exhibited a gravimetric energy density of 33 J g−1. The latter value is about two times higher than the energy densities obtainable for a symmetric PPy–cellulose device as a result of the larger cell voltage range accessible. The capacitance obtained for the asymmetric devices at a current density of 156 mA cm−2 was 11 F g−1 and cycling stability results further indicate that the capacity loss was about 23% during 1000 cycles employing a current density of 20 mA cm−2. The present results represent a significant step forward towards the realization of all-organic material based supercapacitors with aqueous electrolytes and commercially viable capacitances and energy densities.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Polymers for Electrochemical Energy Storage

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...