Inhibition profiles of mono- and polyvalent FimH antagonists against 10 different Escherichia coli strains†
Abstract
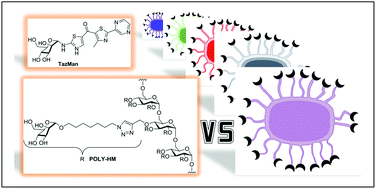
Mono- and polyvalent ligands with strong affinities for the mannose-binding adhesin FimH were synthesised, and their anti-adhesive properties against ten E. coli strains were compared in two cell-based assays. The compounds were assessed against the non-pathogenic E. coli K12 and nine strains isolated by coproculture or from patients with osteoarticular infections (OIs), Crohn's disease (CD) and urinary tract infections (UTIs). The results showed that the compounds could inhibit the whole set of bacterial strains but with marked differences in terms of effective concentrations. The relative inhibitory potency of the monovalent compounds was also conserved for the ten strains and in the two assays. These results clearly suggest that a potent monovalent anti-adhesive assessed on a single E. coli strain will probably be effective on a broad range of strains and may treat diverse E. coli infections (OIs, CD and UTIs). In contrast, the polyvalent compounds showed a significant strain-dependancy in preventing E. coli attachment to intestinal cells. The multivalent antiadhesive effect may therefore vary depending on the E. coli strain tested.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Multivalent Biomolecular Recognition

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...