One-step synthesis of Ni-doped SnO2 nanospheres with enhanced lithium ion storage performance†
Abstract
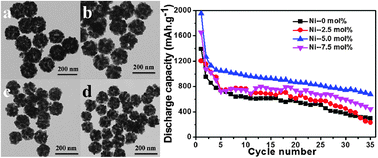
In our work, Ni-doped SnO2 nanospheres have been synthesized via a one-step hydrothermal method using glucose as the soft template. Their structure and physicochemical properties were investigated using X-ray diffraction (XRD), a transmission electron microscope (TEM), a field-emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM) equipped with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) and electrochemical methods. Compared with the pristine SnO2, appropriate Ni-doped SnO2 nanospheres showed much better rate capability and excellent cycling performance. In particular, the sample with 5 mol% Ni showed a high initial reversible capacity of 1267 mA h g−1 at a charge–discharge rate of 0.2 C, and a stable reversible capacity of 674.8 mA h g−1 after 35 cycles. Nickel doping could accommodate the huge volume expansion and avoid the agglomeration of nanoparticles. Thus, the electrochemistry performance was significantly improved.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...