Nonlinear effects in infrared action spectroscopy of silicon and vanadium oxide clusters: experiment and kinetic modeling†
Abstract
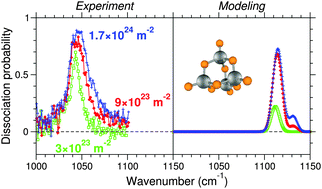
For structural assignment of gas phase compounds, infrared action spectra are usually compared to computed linear absorption spectra. However, action spectroscopy is highly nonlinear owing to the necessary transfer of the excitation energy and its subsequent redistribution leading to statistical ionization or dissociation. Here, we examine by joint experiment and dedicated modeling how such nonlinear effects affect the spectroscopic features in the case of selected inorganic clusters. Vibrational spectra of neutral silicon clusters are recorded by tunable IR-UV two-color ionization while IR spectra for cationic vanadium oxide clusters are obtained by IR multiphoton absorption followed by dissociation of the bare cluster or of its complex with Xe. Our kinetic modeling accounts for vibrational anharmonicities, for the laser interaction through photon absorption and stimulated emission rates, as well as for the relevant ionization or dissociation rates, all based on input parameters from quantum chemical calculations. Comparison of the measured and calculated spectra indicates an overall agreement as far as trends are concerned, except for the photodissociation of the V3O7+–Xe messenger complex, for which anharmonicities are too large and poorly captured by the perturbative anharmonic model. In all systems studied, nonlinear effects are essentially manifested by variations in the intensities as well as spectral broadenings. Differences in some band positions originate from inaccuracies of the quantum chemical data rather than specific nonlinear effects. The simulations further yield information on the average number of photons absorbed, which is otherwise unaccessible information: several to several tens of photons need to be absorbed to observe a band through dissociation, while three to five photons can be sufficient for detection of a band via IR-UV ionization.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Optical spectroscopy coupled with mass spectrometry methods

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...