Branched dimerization of Tat peptide improves permeability to HeLa and hippocampal neuronal cells†
Abstract
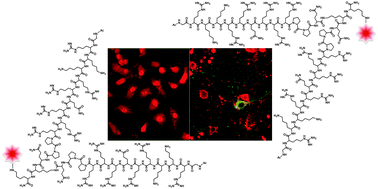
A dimeric branched peptide TATp-D designed as an analogue of the HIV-Tat protein transduction domain (TATp), a prototypical cell penetrating peptide (CPP), demonstrates significantly enhanced cell uptake at 0.25 to 2.5 μM. Live cell confocal laser scanning microscopy revealed that multivalency dramatically improved the permeation potency of TATp-D to HeLa and primary hippocampal neuronal cells. The observed enhanced ability of TATp-D to translocate through the membrane is highlighted by a non-linear dependence on concentration, exhibiting the greatest uptake at sub-micromolar concentrations as compared to TATp. Multimerization via bis-Fmoc Lysine offered a synthetically straightforward method to investigate the effects of multivalent CPPs while offering orthogonal handles for cargo attachment, increasing the utility of CPPs at significantly lower concentrations.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2015 Emerging Investigators

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...