Rapid screening of antibody–antigen binding using dynamic light scattering (DLS) and gold nanoparticles
Abstract
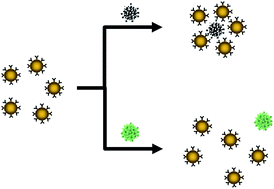
A rapid one-step screening method to evaluate the specificity of antibody–antigen binding was developed using antibody-conjugated gold nanoparticles (Ab–AuNPs) and dynamic light scattering (DLS). Influenza A virus was used as a model antigen to develop this platform and antigen-specific antibodies were attached to the surface of AuNPs. Introduction of virus to the nanoparticle solution resulted in aggregation of the AuNP probes provided that the antibody had an affinity for the virus. A fundamental concern of the work was to ensure aggregates only formed in the presence of the antigen. Therefore, optimal conditions for synthesizing and maintaining the stability of the Ab–AuNP conjugates were investigated by varying pH and antibody concentration, and a protocol for preparing stable Ab–AuNP conjugates is presented. Thereafter the AuNP probes were exploited in a DLS assay to screen the binding specificity of four antibodies to two different isolates of influenza virus (subtype H1N1). The DLS data for antibody binding were in concordance with the results obtained with a conventional ELISA, thereby validating the DLS platform. Importantly, the DLS assay was completed in 30 minutes relative to 24 hours via ELISA.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Emerging Investigators

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...