Nanopipette delivery: influence of surface charge†
Abstract
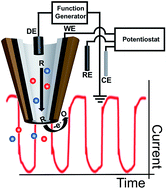
In this report, transport through a nanopipette is studied and the interplay between current rectification and ion delivery for small pipettes is examined. First, surface charge dependence of concentration polarization effects in a quartz nanopipette was investigated. Electrical characterization was performed through current–potential (I–V) measurements. In addition, fluorescein (an anionic fluorescent probe) was utilized to optically map ion enrichment and ion depletion in the nanopipette tip. Bare nanopipettes and polyethylenimine (PEI)-modified nanopipettes were examined. Results confirm that concentration polarization is a surface charge dependent phenomenon and delivery can be controlled through modification of surface charge. The relationship between concentration polarization effects and voltage-driven delivery of charged electroactive species was investigated with a carbon ring/nanopore electrode fabricated from pyrolyzed parylene C (PPC). Factors such as surface charge polarity of the nanopipette, electrolyte pH, and electrolyte concentration were investigated. Results indicate that with modification of surface charge, additional control over delivery of charged species can be achieved.
- This article is part of the themed collection: From nanopores to nanochannels

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...