A glucose-powered antimicrobial system using organic–inorganic assembled network materials†
Abstract
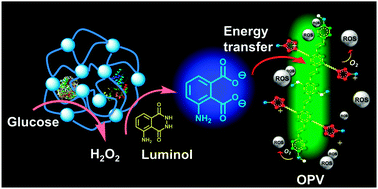
A new glucose-driven photodynamic antimicrobial system was developed to efficiently kill bacteria and fungi, taking advantage of organic–inorganic network materials encapsulating glucose oxidase and horseradish peroxidase and bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...