Molecular design for a cybotactic nematic phase
Abstract
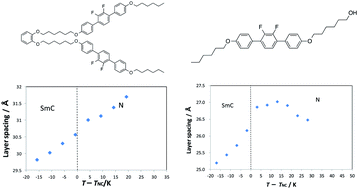
The cybotactic nematic phase (Ncyb) has attracted much attention. However, almost all molecules in which it has been investigated have had a bent-shaped structure. We designed a U-shaped compound, and some rod-like compounds which possessed a terminal hydroxyl group. We then investigated their phase transition behaviour using polarized optical microscopy, differential scanning calorimetry, and X-ray diffraction. The U-shaped compound possessing two 1,4-diphenyl-2,3-difluorobenzene units was found to exhibit an Ncyb phase, with a temperature range of 20 K and a smectic C (SmC) phase. The layer spacing in these phases decreased continuously with decreasing temperature. The rod-like compound, 4-[4-(6-hydroxyhexyloxy)phenyl]-1-(4-hexyloxyphenyl)-2,3-difluorobenzene, was found to exhibit an Ncyb phase with a temperature range of 25 K and an SmC phase. The layer spacing showed a discontinuous decrease at the Ncyb–SmC transition. This report presents two approaches for producing an Ncyb phase, i.e., (1) the introduction of a lateral correlation in the U-shaped compounds and (2) the introduction of different terminal groups in the rod-shaped compounds.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2014 Journal of Materials Chemistry C Hot Articles

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...