Highly-active direct Z-scheme Si/TiO2 photocatalyst for boosted CO2 reduction into value-added methanol
Abstract
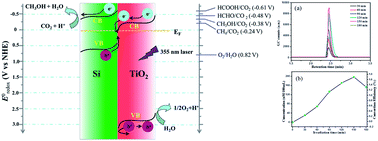
In the present study, direct Z-scheme Si/TiO2 photocatalyst was synthesized via a facile hydrothermal reaction using tetrabutyl titanate and Si powder prepared from magnesiothermic reduction of SiO2 nanospheres. The Si/TiO2 nanospheres were composed of porous Si nanospheres with a diameter of ∼300 nm and TiO2 nanosheets with a diameter of 50 nm and thickness of 10 nm, and demonstrated superior visible light harvesting ability to either Si nanospheres or TiO2 nanosheets. CO2 photocatalytic reduction proved that Si/TiO2 nanocomposites exhibit high activity in conversion of CO2 to methanol with the maximum photonic efficiency of 18.1%, while pure Si and TiO2 catalyst are almost inactive, which can be ascribed to the integrated suitable band composition in the Si/TiO2 Z-scheme system for CO2 reduction. The enhanced photocatalytic property of Z-scheme Si/TiO2 nanospheres was ascribed to the formation of Si/TiO2 Z-scheme system, which improved the separation efficiency of the photogenerated carriers, prolonged their longevity, and therefore boosted their photocatalytic activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...