Friction of aromatic thiol monolayers on silver: SFA and AFM studies of adhesive and non-adhesive contacts†
Abstract
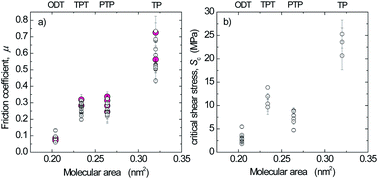
The boundary friction of aromatic thiol (thiophenol, p-phenylthiophenol, and p-terphenylthiol) and octadecanethiol self-assembled monolayers on template-stripped silver was measured under adhesive and non-adhesive conditions with the Surface Forces Apparatus (SFA) and Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM). In non-adhesive contacts, the friction force increased linearly with load. Friction coefficients obtained with the two techniques were in good agreement and decreased with increasing packing density of the aromatic monolayers, but did not reach the low value obtained for octadecanethiol. The sublinear increase in friction force vs. load in adhesive contacts was evaluated as critical shear stresses based on nominal contact areas directly measured with the SFA and calculated using the Thin-Coating Contact Mechanics model for the AFM. The same trend was found in the shear stresses as in the friction coefficients.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Tribology

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...