Tribological study of hydrolytically stable S-containing alkyl phenylboric esters as lubricant additives
Abstract
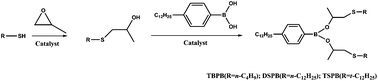
Three novel S-containing alkyl phenylboric esters, i.e., DSPB, TSPB and TBPB, were prepared and characterized. Compared with common boric esters, these three additives exhibit significant hydrolytic stability, which can be attributed to their specific molecular structures, in which a phenyl group conjugates with an electron-deficient boron that helps improve the hydrolytic stability of boric esters. The tribological properties were evaluated using a four ball tester, which suggests that all the synthesized compounds act as anti-wear additives and have relatively high load-carrying capacities. In particular, it should be noted that, among the synthesized compounds, DSPB exhibits both anti-wear and friction-reducing properties. Furthermore, the worn surface was investigated by X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy (XANES). The results demonstrate that the resulting tribofilm consists of trigonal and tetragonal coordination boron, iron sulfide and disulfide, and iron sulfate. Moreover, atomic force microscopy (AFM) was used to characterize the morphology of the tribofilm and the large pads elongated and orientated in the sliding direction were observed, which contribute to the anti-wear (AW) and extreme pressure (EP) performances.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Tribology

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...