Acid-induced formation of hydrogen-bonded double helix based on chiral polyphenyl-bridged bis(2,2′-bipyridine) ligands†
Abstract
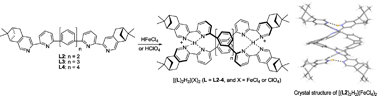
A series of chiral polyphenyl-bridged bis(2,2′-bipyridine) ligands comprising one to four phenyl units were synthesized. The ligands give a weak signal in the CD spectra, but upon addition of tetrachloroferric acid or perchloric acid, a more intense CD signal is observed for ligands having two or more phenyl units. Titration experiments show that the CD signal comes from a monoprotonated species which gives broadened and upfield shifted 1H NMR signals. Variable temperature NMR experiments split the broadened signals into two sets of signals when the temperature is decreased. One of the sets is remarkably upfield while the other has chemical shifts similar to those of the free ligand. The X-ray crystal structures of a free ligand (mono phenyl), a monoprotonated ligand (biphenyl) and a biprotonated ligand (tetraphenyl) were obtained and the structure of the monoprotonated ligand shows that it is a double-stranded helix, which is stabilized by interior hydrogen bonding between the pyridinium N–H and the pyridine N of another ligand strand, and exterior CH⋯Cl hydrogen bonding between FeCl4− and the two ligand strands. Theoretical DFT calculations show that there is such stabilization in solution as well. With the perchlorate anion, the helix formation process is reversible with Et3N which accompanies an on/off CD signal change.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Supramolecular chemistry: self-assembly and molecular recognition

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...