Impact of alloying and lattice strain on ORR activity of Pt and Pd based ternary alloys with Fe and Co for proton exchange membrane fuel cell applications†
Abstract
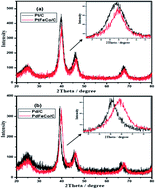
A novel structure–catalytic activity correlation of platinum and palladium alloys is reported in this study. Metals with similar covalent radius (Pt and Pd) were alloyed with metals of lesser covalent radius (Fe and Co). The ternary alloys namely, PtFeCo and PdFeCo were synthesized by a solvothermal method. The structural properties such as lattice parameters and compressive strain of these electrocatalysts were evaluated by XRD and SAED analysis. Particle size and pattern of dispersion of these catalysts in Vulcan XC-72 carbon were characterized by TEM. The composition of the alloys was identified by ICP-OES and EDX techniques. Electrochemical properties such as ECSA, oxygen reduction reaction activity and kinetic parameters were assessed by CV and RDE studies. Structural and electroactivity of both alloys were compared with their respective bulk metal catalysts (20 wt% Pt/C, 20 wt% Pd/C). The lattice strain was calculated from the decrease in lattice parameters of alloys compared with those of pure metals. It is observed that PdFeCo/C shows more compressive strain than PtFeCo/C which is reflected in the greater improvement in ORR activity than that of PtFeCo/C catalyst. ORR studies revealed that both alloys and their pure metals follow a four electron transfer mechanism. The kinetic parameters such as mass and specific activities are calculated from the Tafel slope of ORR. Pt/C, PtFeCo/C and PdFeCo/C electrocatalysts have Tafel slope values (∼120 mV dec−1) indicative of one electron transfer as the rate determining step. The mass and specific activities of PdFeCo/C show higher increments than those of PtFeCo/C compared to their respective metals. The results of ORR studies reflect that lattice strain is an important factor to improve the catalytic activity of the electrocatalyst. Single cell polarizations were carried out at 60, 70 and 80 °C with PtFeCo/C and PdFeCo/C as cathode electrocatalysts. Both ternary alloy electrocatalysts show higher performance than pure metal catalysts. At 80 °C, PtFeCo/C and PdFeCo/C register a power density of 713 mW cm−2 and 437 mW cm−2 respectively.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nanoscience and nanotechnology in electrochemistry

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...