Gallic acid and gallic acid-loaded coating involved in selective regulation of platelet, endothelial and smooth muscle cell fate
Abstract
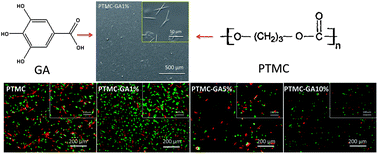
The drug-eluting stent (DES) is the most common means for the treatment of severe coronary heart disease in the clinic. However the DES has some drawbacks, these are long-term endothelial dysfunction, non selective cytotoxicity and late stent thrombosis. Hence, it is significantly important to find a drug or molecule with selective cytotoxicity for the DES. In this work, the effect of gradient concentration of gallic acid on endothelial and smooth muscle cells was investigated through alone-culture and co-culture methods. It was demonstrated that gallic acid promoted the growth of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and suppressed the proliferation of human umbilical artery smooth muscle cells (HUASMCs) at the concentration of ∼5 μg ml−1. Then, gallic acid was mixed into poly(1,3-trimethylene carbonate) to prepare GA-loaded PTMC film via solvent evaporation. And material characteristics and biological evaluations are carried out by different means. These results showed that the GA-loaded PTMC film inhibited the adhesion and activation of platelets, indicating a good anticoagulant performance. Also, this film with a certain GA loading (∼1 wt%) provided significant enhancement for the adhesion and proliferation of HUVECs and inhibition of the growth of HUASMCs. These data suggested the large potential of GA for drug-eluting stent and other vascular devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...