Protein conformation as a regulator of cell–matrix adhesion
Abstract
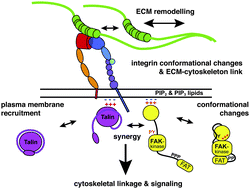
The dynamic regulation of cell–matrix adhesion is essential for tissue homeostasis and architecture, and thus numerous pathologies are linked to altered cell–extracellular matrix (ECM) interaction and ECM scaffold. The molecular machinery involved in cell–matrix adhesion is complex and involves both sensory and matrix-remodelling functions. In this review, we focus on how protein conformation controls the organization and dynamics of cell–matrix adhesion. The conformational changes in various adhesion machinery components are described, including examples from ECM as well as cytoplasmic proteins. The discussed mechanisms involved in the regulation of protein conformation include mechanical stress, post-translational modifications and allosteric ligand-binding. We emphasize the potential role of intrinsically disordered protein regions in these processes and discuss the role of protein networks and co-operative protein interactions in the formation and consolidation of cell–matrix adhesion and extracellular scaffolds.
- This article is part of the themed collection: The free energy landscape: from folding to cellular function

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...