Electron impact induced anion production in acetylene
Abstract
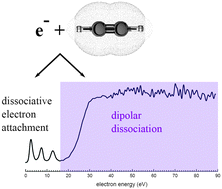
A detailed experimental investigation of electron induced anion production in acetylene, C2H2, in the energy range between 1 and 90 eV is presented. The anions are formed by two processes in this energy range: dissociative electron attachment (DEA) and dipolar dissociation (DD). DEA in C2H2 is found to lead to the formation of H− and C2−/C2H− through excitation of resonances in the electron energy range 1–15 eV. These anionic fragments are formed with super thermal kinetic energy and reveal no anisotropy in the angular distributions. DD in C2H2 leads to the formation of H−, C−/CH− and C2−/C2H− with threshold energies of 15.7, 20.0 and 16.5 eV respectively. The measured anion yields have been used to calculate anion production rates for H−, C−/CH− and C2−/C2H− in Titan's ionosphere.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Astrochemistry

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...