Equilibrium thermodynamics and folding kinetics of a short, fast-folding, beta-hairpin†
Abstract
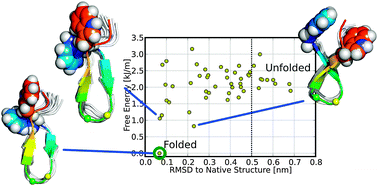
Equilibrium thermodynamics of a short beta-hairpin are studied using unbiased all-atom replica exchange molecular dynamics simulations in explicit solvent. An exploratory analysis of the free energy landscape of the system is provided in terms of various structural characteristics, for both the folded and unfolded ensembles. We find that the favorable interactions between the ends introduced by the tryptophan cap, along with the flexibility of the turn region, explain the remarkable stability of the folded state. Charging of the N termini results in effective roughening of the free energy landscape and stabilization of non-native contacts. Folding–unfolding dynamics are further discussed using a set of 2413 independent molecular dynamics simulations, 2 ns to 20 ns long, at the melting temperature of the beta-hairpin. A novel method for the construction of Markov models consisting of an iterative refinement of the discretization in reduced dimensionality is presented and used to generate a detailed kinetic network of the system. The hairpin is found to fold heterogeneously on sub-microsecond timescales, with the relative position of the tryptophan side chains driving the selection of the specific pathway.
- This article is part of the themed collection: The free energy landscape: from folding to cellular function

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...