Interatomic Coulombic interactions as the driving force for oriented attachment
Abstract
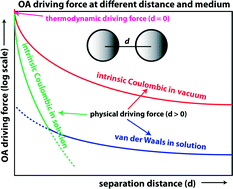
Growth of nano- and mesocrystals in both laboratory and natural environments can proceed via the oriented attachment (OA) pathway. However, the driving force for OA is controversial; surface energy reduction, van der Waals interaction, and/or dipole–dipole interactions have been proposed. Here, we analyzed the interaction energy of two approaching nanoparticles by comparing the magnitudes of Coulombic interactions from molecular energetic calculations, van der Waals interactions from the Hamaker formulation, and surface charge repulsion from the DLVO theory. The analyses were conducted for three materials: SiO2, ZnS and ZnO. Results show that in vacuum, or when two nanoparticles are in close proximity in an electrolyte solution, the strong intrinsic interatomic Coulombic interactions between two nanoparticles provide the primary physical driving force for OA. However, when two particles are far apart in a solution, the interatomic Coulombic interactions are screened and van der Waals interactions become the physical driving force (that superimposes onto the random force from the Brownian motion). In both vacuum and a solution, the energy change that occurs following an OA event (i.e., the thermodynamic driving force) comes largely from the interatomic Coulombic interactions arising from both the surface atoms (accounting for the surface energy reduction) and the atoms in interior of the nanoparticles. This energy change is crystallographic orientation-dependent. The findings of this study indicate the range of conditions under which interatomic Coulombic interactions provide the primary driving force for crystal growth by OA and highlight the effects of aqueous solution and ionic strength on the energetics of the process.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nanocrystal growth via oriented attachment

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...