Designing nanoparticle carriers for enhanced drug efficacy in photodynamic therapy†
Abstract
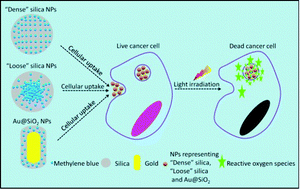
Although nanoparticles (NPs) have been proposed as carriers for photosensitizers (PS) in photodynamic therapy (PDT), how the design parameters of nanocarriers affect the final drug efficacy remains unclear. By designing SiO2-PS NPs with specific features (such as enabling easy release of PS from the nanocarriers, or introducing plasmonic Au NPs in the vicinity of the PS), and comparing the respective efficacy of PS to that of the conventional dense SiO2-PS NPs (PS were tightly confined into the silica matrix), we identified that both PS trapping-in/releasing from the silica nanocarriers and the Au plasmonic effect were responsible for the PS efficacy variation. The mechanistic study also disclosed that the different NP configurations would affect the cellular death pathway. These findings provide a general guideline for the design of NP-based PDT applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...