Digital drug delivery: on–off ultrasound controlled antibiotic release from coated matrices with negligible background leaching
Abstract
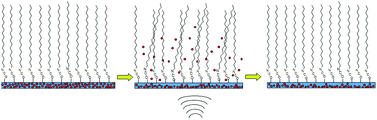
Hydrogels such as crosslinked poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (pHEMA) have been used extensively in controlled release drug delivery systems. Our previous work demonstrated an ultrasound (US)-responsive system based on pHEMA coated with a self-assembled multilayer of C12–C18 methylene chains. The resulting coating was predominantly crystalline and relatively impermeable, forming an US-activated switch that controlled drug release on-demand, and kept the drug within the matrix in the absence of US. The device, as developed did, however, show a low background drug-leaching rate independent of US irradiation. For some applications, it is desirable to have very low or zero background release rates. This was achieved here by a combination of new processing steps, and by co-polymerizing HEMA with a relatively hydrophobic monomer, hydroxypropyl methacrylate (HPMA). These advances produced systems with undetectable ciprofloxacin background release rates that are capable of US-facilitated drug release – up to 14-fold increases relative to controls both before and after US exposure. In addition, these observations are consistent with the hypothesis that US-mediated disorganization of the coating allows a transient flux of water into the matrix where its interaction with bound and dissolved drug facilitates its movement both within and out of the matrix.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...