Ultrafiltration LC-PDA-ESI/MS combined with reverse phase-medium pressure liquid chromatography for screening and isolation potential α-glucosidase inhibitors from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi
Abstract
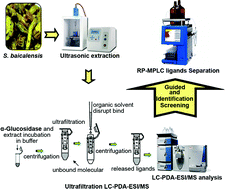
Diabetes mellitus (DM) has become a worldwide health problem. α-Glucosidase inhibitors are widely used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes, and natural products are considered as the promising sources of α-glucosidase inhibitors. In this research, ultrafiltration liquid chromatography with photodiode array detection coupled to electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (Ultrafiltration LC-PDA-ESI/MS) were applied to screen and identify α-glucosidase inhibitors from Scutellaria baicalensis. Following this, reverse-phase medium-pressure liquid chromatography (RP-MPLC) was applied to separate and isolate the active constituents. As a result, eleven major compounds in S. baicalensis were screened and identified as α-glucosidase inhibitors by Ultrafiltration LC-PDA-ESI/MS and six ligands, baicalin, wogonoside, 5,7,3,2′,6′-pentahydroxy flavanone, chrysin-6-C-arabinosyl-8-C-glucoside, chrysin-6-C-glucosyl-8-C-arabinoside and wogonin, were isolated by RP-MPLC. The purities of the six compounds were 89.7%, 83.5%, 76.2%, 93.7%, 75.1% and 96.2%, respectively, as determined by high performance liquid chromatography. The results demonstrate that the method for systematic isolation of bioactive components in S. baicalensis guided by Ultrafiltration LC-PDA-ESI/MS is a feasible and efficient technique and could be expected to extend for the separation of other enzyme inhibitors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...