High-throughput and automatic typing via human papillomavirus identification map for cervical cancer screening and prognosis†
Abstract
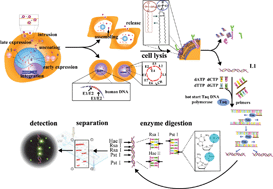
A novel human papillomavirus (HPV) typing assay for cervical cancer screening and prognosis was developed by the combination of restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) and microchip electrophoresis (MCE) to achieve higher levels of sensitivity and throughput. The detection limit of 2 × 102 copies, high sensitivity and typing accuracy on the account of PCR-RFLP-MCE method guarantee the successful diagnosis results of 4-fold higher infection rate over cytologic tests. From clinical samples, eleven kinds of HPV types were identified with a good compatibility degree of over 90%. The described method showed good reliability in clinical samples and provided a promising alternative for pathological studies at the molecular level.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Probe and chip approaches to cell analysis

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...