Ferulic acid protects against methotrexate nephrotoxicity via activation of Nrf2/ARE/HO-1 signaling and PPARγ, and suppression of NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome axis
Abstract
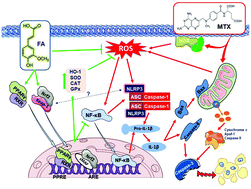
Drug-induced nephrotoxicity contributes to acute kidney injury (AKI) and represents a major problem in the clinical setting. We investigated the possible involvement of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in methotrexate (MTX)-induced nephrotoxicity and the protective potential of ferulic acid (FA), pointing out the role of PPARγ and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Rats that received MTX showed a significant increase in circulating creatinine and urea, and kidney Kim-1 levels along with multiple histological alterations. Reactive oxygen species (ROS), malondialdehyde and nitric oxide levels showed a significant increase in the kidney of rats that received MTX, while antioxidant defenses were diminished. FA ameliorated kidney function markers, prevented histological alterations, suppressed ROS production and enhanced antioxidant defenses. FA inhibited MTX-induced inflammasome activation as showed by the decreased phosphorylation of NF-κB, and expression of NLRP3, caspase-1 and IL-1β. MTX caused apoptosis marked by increased expression of BAX, cytochrome c and caspase-3, and suppressed Bcl-2, effects that were significantly reversed in FA-treated groups. In addition, FA up-regulated Nrf2/ARE/HO-1 signaling and PPARγ expression in the kidney of MTX-induced rats. In conclusion, activation of NLRP3 inflammasome may represent a new mechanism for MTX nephrotoxicity. FA up-regulated PPARγ and Nrf2 signaling, prevented overproduction of ROS, and suppressed NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome axis and apoptosis in the kidney of MTX-induced rats.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...