Composite interfaces of g-C3N4 fragments loaded on a Cu substrate for CO2 reduction†
Abstract
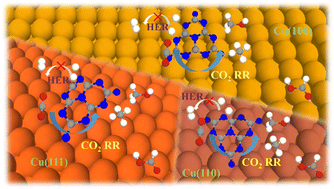
Designing an electrocatalyst with high efficiency and product selectivity is always crucial for an electrocatalytic CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR). Inspired by the great progress of two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterials growing on Cu surfaces and their promising CO2RR catalytic efficiencies at their interfaces, the unique performance of Cu-based 2D materials as high-efficiency and low-cost CO2RR electrocatalysts has attracted extensive attention. Herein, based on density functional theory (DFT) calculations, we proposed a composite structure of graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) fragments loaded on a Cu surface to explore the CO2RR catalytic property of the interface between g-C3N4 and the Cu surface. Three composite interfaces of C3N4/Cu(111), C3N4/Cu(110) and C3N4/Cu(100) have been studied by considering the reaction sites of vertex nitrogen atoms, edge nitrogen atoms and the nearby Cu atoms. It was found that the C3N4/Cu interfaces where nitrogen atoms contact the Cu substrate present competitive CO2RR activity. Among them, C3N4/Cu(111)-N3 exhibited a better activity for CH3OH production, with a low overpotential of 0.38 V. For HCOOH and CH4 production, C3N4/Cu(111)-Cu and C3N4/Cu(100)-N1 have overpotentials of 0.26 V and 0.44 V. The electronic analysis indicates the electron transfer from the Cu substrate to the g-C3N4 fragment and mainly accumulates on the nitrogen atoms of the interface. Such charge accumulation can activate the adsorbed C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bond of CO2 and lead to lower energetic barriers of CO2RR. DFT calculations indicate that the boundary nitrogen sites reduced the energy barrier of *CHO, which is crucial for CO2RR, compared with that of the pristine Cu surface. Our study explores a new Cu-based electrocatalyst and indicates that the C3N4/Cu interface can enhance the activities and selectivity of CO2RR and open a new strategy to design high-efficiency electrocatalysts for CO2RR.
O bond of CO2 and lead to lower energetic barriers of CO2RR. DFT calculations indicate that the boundary nitrogen sites reduced the energy barrier of *CHO, which is crucial for CO2RR, compared with that of the pristine Cu surface. Our study explores a new Cu-based electrocatalyst and indicates that the C3N4/Cu interface can enhance the activities and selectivity of CO2RR and open a new strategy to design high-efficiency electrocatalysts for CO2RR.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...